Why are delivery error rates different between API and UI?

Michael Ko
Co-founder & CEO, Suped
Published 26 May 2025
Updated 5 Nov 2025
7 min read

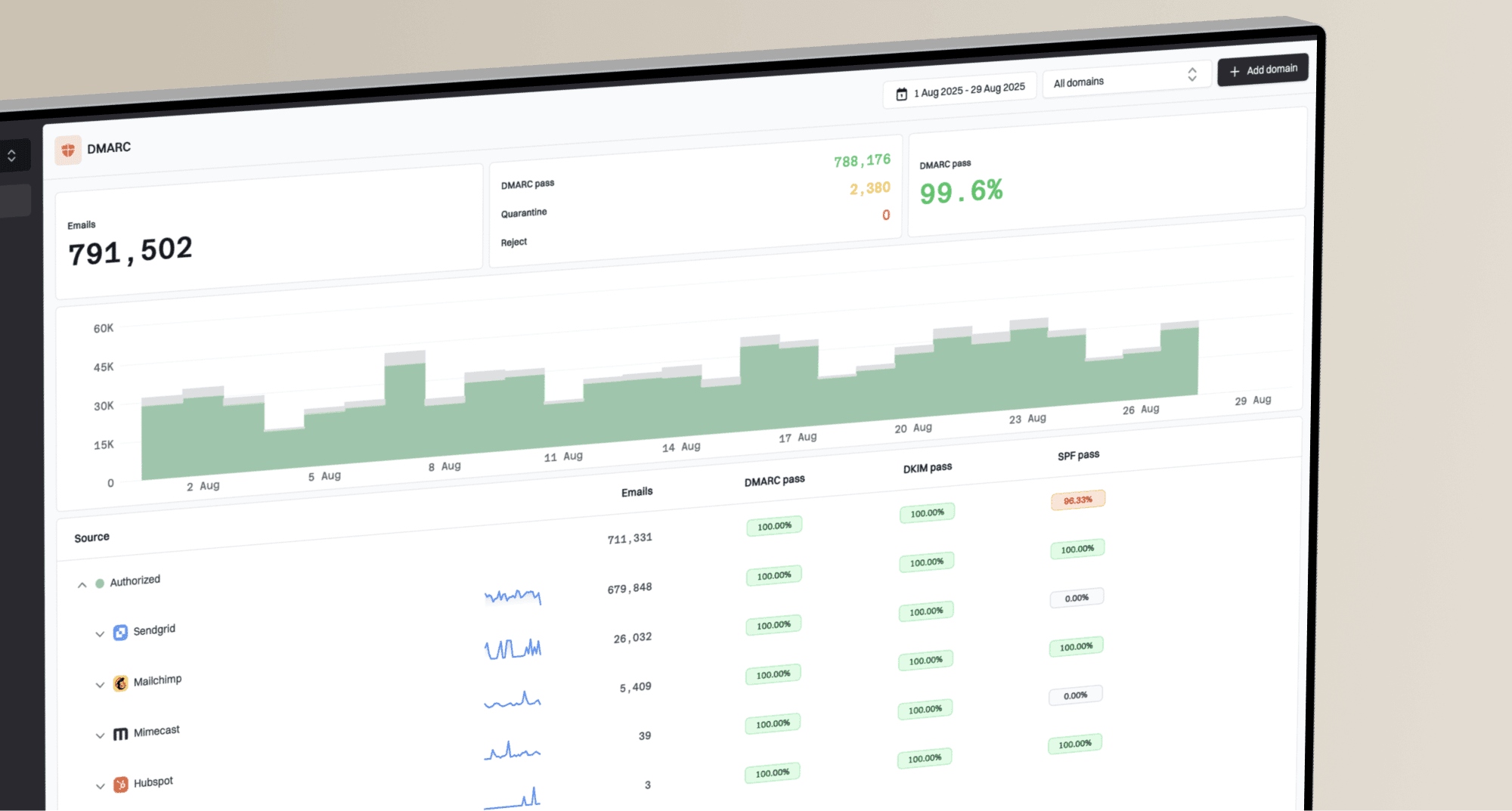
 Google Postmaster Tools (GPT). This isn't just a minor annoyance, it can lead to misinformed decisions about your email strategy and a delay in addressing critical deliverability problems.
Google Postmaster Tools (GPT). This isn't just a minor annoyance, it can lead to misinformed decisions about your email strategy and a delay in addressing critical deliverability problems. Postmaster Tools sometimes redacts data or aggregates it, especially if your sending volume falls below certain thresholds. This means the numbers you see in the UI might be a simplified representation rather than the complete picture available via the API.
Postmaster Tools sometimes redacts data or aggregates it, especially if your sending volume falls below certain thresholds. This means the numbers you see in the UI might be a simplified representation rather than the complete picture available via the API.{ "date": "2024-05-29", "total_emails": 100000, "delivery_errors_percentage": 0.0, "error_details": [ { "error_type": "spam_complaint", "percentage": 0.0 }, { "error_type": "domain_rejection", "percentage": 0.0 } ] }